New expertise may make diabetes administration extra accessible to those that want it most.
Researchers at Peking College have designed a synthetic pancreas 98% smaller and 100 instances cheaper to fabricate than any of the gadgets at present accessible out there.
A synthetic pancreas is an automatic insulin supply system consisting of a sensor that constantly tracks blood sugar ranges, an insulin pump, and an algorithm that calculates how a lot insulin is required at any given second. Any such gadget can considerably enhance the administration of diabetes — each sort 1 and sort 2 — because it shifts the burden of constructing remedy selections a number of instances a day away from the sufferers.
Nonetheless, these gadgets are cumbersome, uncomfortable to put on, and the lengthy needle required for the blood glucose sensor may cause ache in some customers. As well as, the worth of this expertise is at present a significant barrier stopping widespread use.
“So far, there are just a few commercially accessible synthetic pancreas gadgets in the marketplace,” mentioned Yue Cui, affiliate professor at Peking College’s Faculty of Supplies Science and Engineering. “These gadgets are costly, starting from $3,000 to $8,000.”
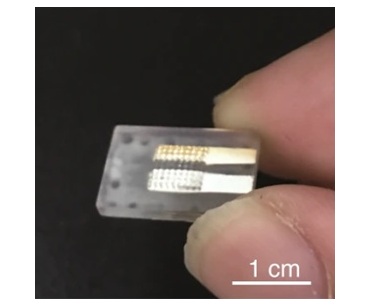
In distinction, the brand new synthetic pancreas designed by Cui and colleagues is compact, straightforward to put on and cheap to fabricate at a price of $10 per unit.
How you can construct a mini synthetic pancreas
Step one to make the miniature synthetic pancreas was to cut back the scale of the glucose sensor. To that finish, the researchers switched the lengthy metallic needle utilized in industrial gadgets with microneedles lower than 1 mm lengthy every, that dissolve away as soon as they’re not wanted. Upon utility, the needles pierce the highest layer of the pores and skin simply sufficient to place in place an array of even smaller microtubes, hooked up to electrodes that the sensor depends on to measure glucose ranges.
One other essential step in the direction of lowering the general dimension of the gadget was to decrease its energy consumption, for the reason that batteries required to energy it take up a sizeable portion of the system. As a result of the insulin pump is the part that consumes probably the most vitality, the scientists switched the normal mechanical pump for an electro-osmotic micropump, which is way smaller and easier. The micropump was additional engineered to cut back the quantity of vitality it consumes, leading to a complete energy utilization greater than 300 instances decrease than a traditional insulin pump.
The glucose sensor, the micropump and a 3D-printed insulin reservoir have been then stacked on high of one another, leading to a tool the scale of a small coin — about 1.5 cm in diameter and 1cm thick. The whole quantity of the gadget is nearly two cubic centimeters, whereas a typical synthetic pancreas at present accessible is usually greater than 100 cubic centimeters massive.
More and more accessible expertise
Experiments in diabetic rats and pigs confirmed the miniature synthetic pancreas may keep secure glucose sensing and insulin pumping over the course of three days. On common, the animals had their blood sugar ranges within the goal vary 68% of the time, in comparison with 75% time in vary for a industrial gadget.
Based mostly on typical revenue margins and price of gross sales for medical gadgets, the researchers estimate that about 40% of the worth of economic gadgets are manufacturing prices, which might put these bills at between $1,000 to $4,000 per gadget. At simply $10 per unit, the manufacturing prices of the miniature synthetic pancreas may make this expertise far more accessible to customers the world over.
Future work will deal with bettering the efficiency of the gadget whereas additional lowering its dimension and energy utilization. As a way to put together the gadget for use in a medical setting, the scientists may even work on bettering the management algorithms that calculate how a lot insulin is required at any given second, in addition to making the smartphone interface extra consumer pleasant.
“Contemplating all these optimized processes and the time wanted for FDA approval, it’s estimated to be 3–5 years for the gadget to be virtually used sooner or later,” mentioned Cui. “We anticipate that this work would provide necessary contributions to digital well being and wearable gadgets for diabetes sufferers, and have the potential to revolutionize typical diabetes administration towards at-home healthcare.”
Reference: Yiqun Liu et al., Closed-Loop Bioelectronic Artificial Pancreas Patch for Continuous Monitoring and Regulation of Blood Glucose in Diabetic Rats and Pigs, Superior Science (2025). DOI: 10.1002/advs.202503536


