Engineers have developed tactile sensors with elevated sensitivity, due to auxetic mechanical metamaterials.
Engineers have developed tactile sensors with elevated sensitivity, due to auxetic mechanical metamaterials.
Tactile sensors are widespread amongst applied sciences corresponding to touchscreens, touchpads, smartwatches, and health trackers. These sensors convert bodily stimuli, corresponding to strain or pressure, into {an electrical} response throughout the system. Past client electronics, tactile know-how is extremely related for superior prosthetics, industrial robotics, safety programs, and healthcare units that give suggestions on the customers’ bodily actions for well being monitoring.
Mechanical metamaterials (MMs) have gained reputation for constructing tactile sensors and actuators due to the tunability of a variety of their bodily properties. These will be launched by tweaking their periodic mobile architectures to pay attention or amplify the strain utilized to the sensor.
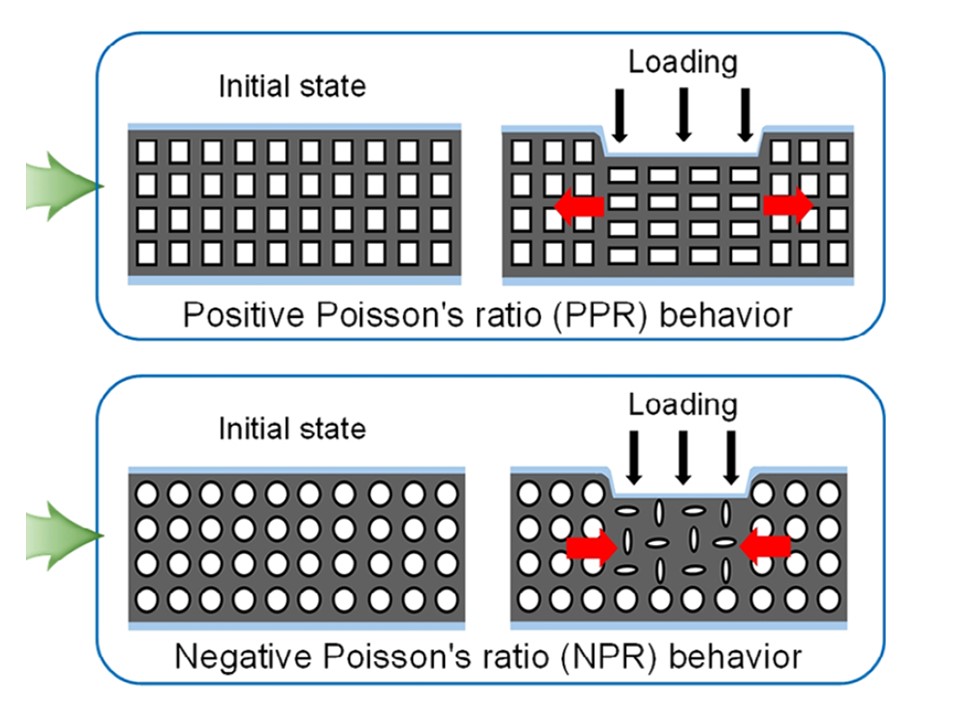
and a adverse Poisson’s ratio materials. Picture credit score:
Mingyu Kang et al., doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202509704.
Curiously, a class of MMs known as auxetic mechanical metamaterials (AMMs) displays adverse Poisson’s ratio, i.e., when compressed, they have an inclination to contract laterally as a substitute of increasing. Prof. Soonjae Pyo’s workforce at Seoul Nationwide College of Science and Expertise used digital gentle processing, a 3D printing approach for curing photopolymerizable supplies layer-by-layer, to develop silicon rubber-based AMMs comprising specifically arranged spherical voids in a cubic lattice. The joints round these spherical voids facilitate the above-mentioned lateral contraction as they have an inclination to bear rotational deformation below utilized stress.
The workforce constructed two sorts of tactile sensors primarily based on such AMMs: capacitive sensors, that reply on to strain modulation, and a carbon nanotube (CNT)-coated resistive sensor (C-AMM) that responds to modifications in resistance in a fabric when deformed. A capacitive sensor is usually extra delicate to small modifications in strain, whereas a resistive sensor is favorable for detecting bigger pressures, thereby complementing one another.
Exploring a doable actual world utility, the workforce developed a resistive sensor by making a sensor array, whereby 16 C-AMM items are organized in a grid of 4 rows and 4 columns every, making a 16-pixel grid, every built-in between custom-built electrodes.. Such an array was subjected to different ranges of stress from non-contact to a number of factors to evaluate its sensitivity and spatial discrimination. Additional, the researchers developed a sensible insole comprising a pair of electrodes and C-AMM sensor arrays sandwiched inside polymeric movies, which they put in in sneakers for gait monitoring and pronation evaluation whereas the consumer is out for a stroll.
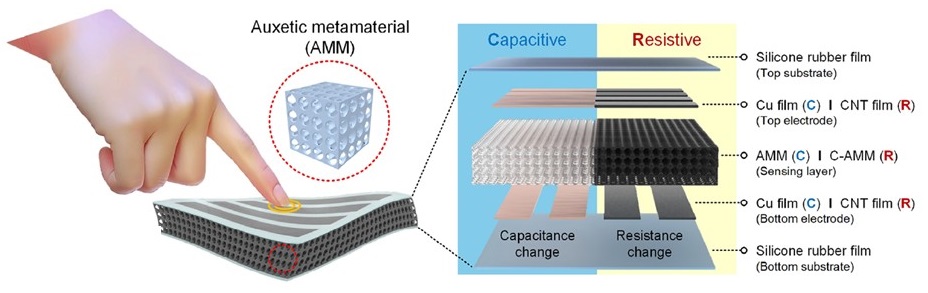
This analysis presents what the authors name a “structure-centric design strategy, decoupled from particular materials decisions,” which may function a technique for constructing personalized tactile sensors able to higher pressure focus and power dissipation for the improved sensitivity of prosthetics, biomedical units for well being monitoring, and lengthening the capabilities of robots.
Featured Picture Credit score: Gordon Johnson through Pixabay


