pH-responsive surfactants allow management over buckled supraparticle formation in emulsion-based techniques.
Supraparticles are clusters of smaller constructing blocks, usually nanoparticles or molecules, for which the collective behaviour can produce attention-grabbing and emergent properties. The brand new functionalities that come up from this behaviour could be exploited for additive manufacturing, meals science, absorption, catalysis, prescription drugs, and as stabilisers in fluid techniques.
Tailoring supraparticle properties for such assorted functions requires management over the properties of the person particles, and one of the best ways to govern that is to direct how they assemble.
Meeting of Supraparticles
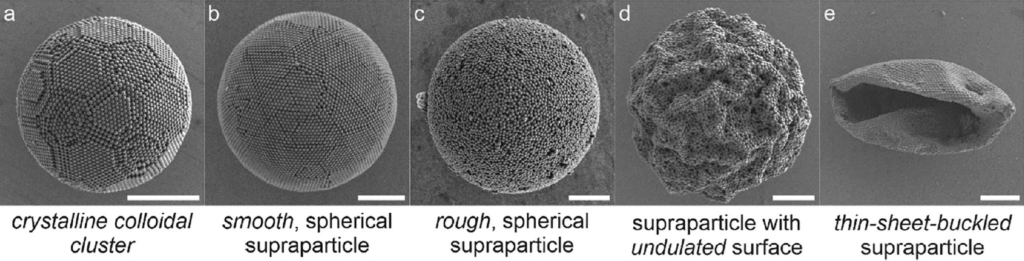
As a droplet filled with nanoscale constructing blocks dries, these nanoparticles are pressured nearer and nearer collectively and self-organise (assemble) into supraparticles. The ultimate construction of that meeting relies on how the droplet dries. If the nanoparticles are free to diffuse by means of the majority liquid, spherical supraparticles kind; the place the method is intentionally slowed, the result’s extremely ordered minimum-energy constructions.
Shorter drying instances, alternatively, initially result in spheres with ordered floor constructions, till a threshold velocity is reached. Below very quick drying circumstances, the nanoparticles are not capable of diffuse shortly sufficient by means of the majority liquid, and they also accumulate on the interface to kind hole particles with a dense, buckled shell. This buckling distorts the form of the ultimate supraparticle, creating undulating surfaces and, finally, absolutely collapsed shell constructions.
Controlling the drying velocity of the droplet (the ‘droplet kinetics’) due to this fact allows management over the ultimate form and construction of the supraparticle and, thus, its performance.
When Kinetics Fails: Supraparticles from Emulsions
Utilizing kinetics to manage supraparticle formation doesn’t work the identical approach for emulsion-based techniques – techniques of liquids that don’t combine, like water and oil, the place one liquid exists as droplets inside the different. In such techniques, management over supraparticle meeting has to return from a unique phenomenon: the place the person nanoparticles need to go.
Think about each doable response in a system as a pathway. Some pathways are steep and rocky, and it takes extra effort to journey them; some have a extra mild slope and are simpler to navigate. The latter, extra beneficial, pathways symbolize reactions which can be extra prone to occur. For those who can management how beneficial a response pathway is (controlling the ‘thermodynamics’ of the system), then you will have management over which reactions are probably to happen.
You may direct the system to do what you need it to.
Researchers can use this trick to direct supraparticle formation in emulsion-based techniques, exploiting thermodynamics to make sure that probably the most beneficial motion for the nanoparticles is to go to the water/oil interface. The drying droplet then acts as a template for his or her meeting into skinny shells, producing simply the best circumstances for buckling.
Governing this affinity for the interface are the interactions between the nanoparticles and the encompassing liquids, however colloidal nanoparticles aren’t eager on the fluorinated oils usually used for microfluidic emulsions, which means that they like to not stay on the interface for lengthy in such techniques.
This could stop buckled supraparticle formation and, but, for such techniques, buckled supraparticles are being noticed.
The Magic Ingredient
Water and oil received’t combine however, should you mix them and shake effectively, many small bubbles of 1 will diffuse inside the different. Slowly, the 2 incompatible liquids will separate out once more, with the oil layer lastly floating above the water layer. To forestall this separation and hold emulsions secure, surfactants are added – molecules that may bridge water- and oil-based substances, similar to these utilized in washing detergents.
Nicolas Vogel and colleagues at Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg (FAU, Germany) and École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL, France) explored how these same surfactants can also make the interface a more favourable destination for nanoparticles in emulsion techniques with fluorinated oils.
They used charged polystyrene constructing blocks and pH-responsive surfactants, which might be altered by adjusting the pH of the system. This affected their electrostatic interactions with the charged particles and, consequently, the affinity of these particles for the droplet/oil interface. Supraparticles that shaped below circumstances of stronger repulsion (negatively charged particles and a negatively charged surfactant) took on a spherical form; with poor repulsion and even weak attraction between the polystyrene and the surfactant, the polystyrene most well-liked to adsorb on the interface, resulting in buckled supraparticle constructions.
Predicting Supraparticle Morphology
The mechanism behind the surprising buckling of those supraparticles is now clear… however the implications of this examine transcend simply an attention-grabbing rationalization.
For superb management over the templating of supraparticles in these tough emulsion techniques, the group recognised that the native pH circumstances within the water droplets change over time: by deciding on the response time at which the polystyrene particles favoured the interface, they might tune the extent of the buckling and, thus, the ultimate supraparticle morphology.
Their resolution is particularly elegant as a result of the water/oil system they selected is effectively established, which means that these findings could be broadly utilized to ongoing supraparticle manufacturing processes with little disruption.
“These insights,” state the researchers with none trace of hyperbole, “present easy handles to reliably management the morphology”. As is usually agreed, and as you may additionally agree when trying on the photographs of their particles (determine above), easy is gorgeous.


