Synthetic intelligence instruments matched or exceeded human attorneys in producing dependable contract drafts within the first complete benchmarking research evaluating AI towards authorized professionals, in accordance with analysis revealed this week.
The research, Benchmarking Humans & AI in Contract Drafting, performed by LegalBenchmarks.ai, discovered that human attorneys produced dependable first drafts 56.7% of the time, whereas a number of AI merchandise met or exceeded their efficiency.
The highest-performing AI device, Gemini 2.5 Professional, achieved a 73.3% reliability charge, marginally outperforming the most effective human lawyer at 70%.
The analysis evaluated 13 AI instruments towards human attorneys utilizing 30 real-world contract drafting duties. The research assessed 450 job outputs and surveyed 72 authorized professionals to measure three dimensions of efficiency: output reliability, usefulness, and workflow integration.
Of the 13 instruments evaluated, seven had been instruments designed particularly for the authorized market: August, Brackets, GC AI, InstaSpace, SimpleDocs and Wordsmith. One of many seven was not recognized by title, however was described as a “long-standing enterprise legal-ai platform.”
The opposite six had been normal business instruments: ChatGPT (GPT-4.1 and GPT-5), Claude (Opus-4.1), Copilot (free model), Gemini (2.5 Professional), Le Chat(Mistral), and Qwen (qwen3-235b-a22b).
AI Identifies Authorized Dangers Legal professionals Missed
In situations involving excessive authorized dangers, specialised authorized AI instruments outperformed normal objective instruments, elevating specific danger warnings in 83% of outputs, in comparison with 55% for normal instruments. Nevertheless, in the identical situations, human attorneys raised no such warnings, in accordance with the research.
“Authorized AI instruments surfaced materials dangers that attorneys missed completely,” the researchers wrote. In a single instance involving a probably unenforceable penalty clause below New York legislation, AI instruments flagged enforceability considerations whereas human attorneys supplied no danger evaluation.
The findings problem assumptions about AI’s incapability to train authorized judgment, the researchers stated, displaying that some AI instruments can establish compliance and enforceability points neglected by skilled practitioners.
Instruments Differ In Efficiency
The research revealed substantial variations in AI efficiency. Reliability charges ranged from 44% to 73.3% throughout totally different instruments. Google’s Gemini 2.5 Professional achieved the very best reliability rating, adopted by OpenAI’s GPT-5 at roughly 73%.
Authorized AI platforms, together with GC AI, Brackets, August, and SimpleDocs, additionally scored above the general AI common of 57%. Common-purpose AI instruments barely outperformed specialised authorized AI platforms on reliability metrics, opposite to what many within the trade may anticipate.
In usefulness rankings, August led with a median rating of 8.13 out of 9 factors, whereas human attorneys averaged 7.53 factors. The metric measured readability, helpfulness and acceptable size of draft outputs.
“Specialised authorized AI instruments didn’t meaningfully outperform general-purpose AI instruments in each output reliability and usefulness,” the researchers stated. “Common-purpose AI options had a slight edge in output reliability, whereas authorized AI options scored marginally greater on output usefulness.”
Workflow Integration As Differentiator
Whereas general-purpose AI instruments competed successfully on output high quality, specialised authorized AI platforms differentiated themselves via workflow integration. Two-thirds of examined authorized AI merchandise combine with Microsoft Phrase, the place most contract drafting happens.
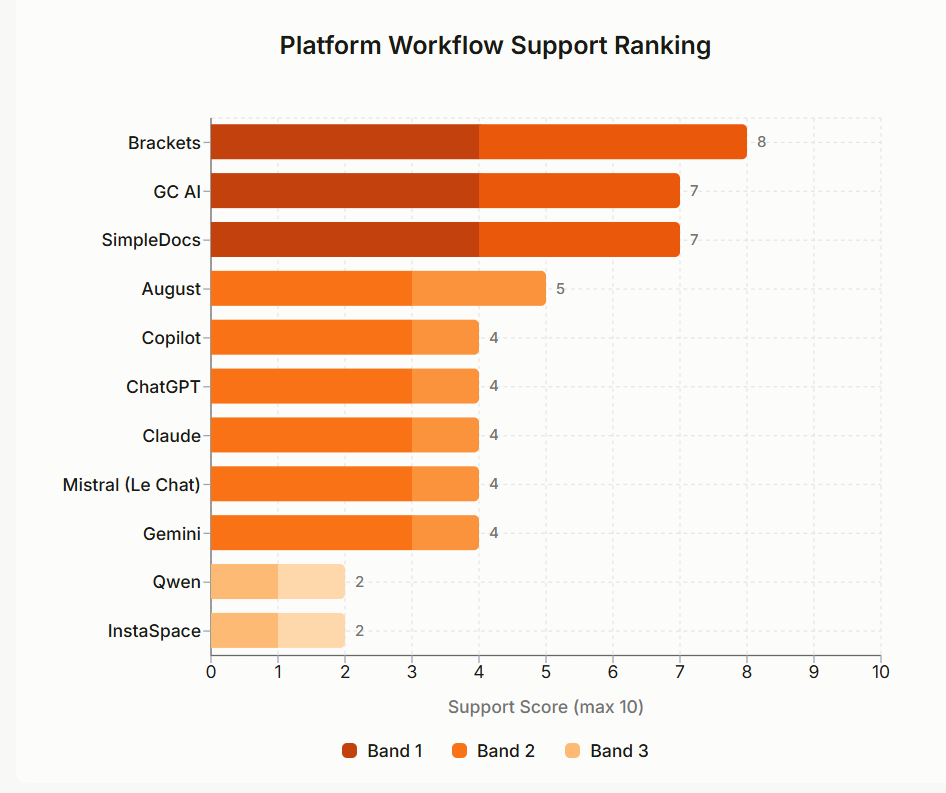
Brackets, GC AI, and SimpleDocs scored highest on platform workflow help, providing options like template libraries, clause storage, and high quality assurance instruments designed particularly for authorized work.
“Platform Workflow Help is the important thing differentiator for specialised instruments, not output efficiency,” the researchers concluded.
People Higher At Advanced Duties
Human attorneys demonstrated clear benefits in duties requiring business judgment and context administration. They excelled at decoding consumer intent, avoiding pointless concessions to counterparties, and integrating a number of data sources.
In a single multi-source drafting job requiring integration of templates, time period sheets and e-mail communications, solely the human lawyer efficiently extracted full get together data from a screenshot. All AI outputs contained incomplete or inaccurate firm particulars.
Nevertheless, AI instruments proved extra constant in routine drafting. In a job requiring a ten% penalty clause, all AI instruments appropriately reproduced the determine whereas one human lawyer mistakenly wrote “9%.”
The starkest differentiator between people and AI was within the size of time it took to finish a job, the report stated. People took almost 13 minutes per job whereas AI instruments produced outputs in seconds.
Altering Skilled Priorities
Among the many 72 attorneys surveyed for the research who use AI for authorized work, 86% make use of a number of instruments quite than counting on a single product. Solely 6% require 100% accuracy earlier than utilizing AI instruments, whereas 55% expressed consolation with accuracy under 90%.
When requested about elements that might enhance AI utilization, 35% cited simpler output verification as most vital, 23% pointed to improved context administration, and 21% ranked accuracy good points as the highest precedence.
“Accuracy is just one of a number of elements we think about,” one Fortune 500 normal counsel advised researchers. “Each lawyer is answerable for reviewing the work product they produce, with or with out AI.”
Methodology and Limitations
The research evaluated AI instruments and human attorneys utilizing equivalent duties contributed by training attorneys throughout varied industries. Duties ranged from fundamental clause drafting to advanced business preparations.
The analysis assessed three efficiency dimensions: output reliability (factual accuracy and authorized adequacy), output usefulness (readability and helpfulness), and platform workflow help (integration and verification options).
The human baseline consisted of in-house business attorneys with a median of 10 years’ expertise. Outputs had been evaluated via a mixture of automated scoring towards predefined standards and professional reviewer evaluation.
The researchers acknowledged a number of limitations, together with the snapshot nature of quickly evolving AI capabilities, the subjective parts in scoring usefulness, and the concentrate on junior- to mid-level drafting complexity.
Backside Line
The underside line appears to be that duties involving routine, low-risk contract drafting could also be the most effective candidates for utilizing AI, whereas advanced business negotiations proceed to require human experience.
“The way forward for drafting is not going to be determined by one facet or one device,” the researchers wrote. “It is going to be formed by orchestration: combining the velocity and consistency of normal AI, the workflow match of authorized AI, and the judgment of attorneys. The actual benefit will belong to groups that be taught to design and handle this collaboration.”
The analysis was performed by Anna Guo, Arthur Souza Rodrigues, Mohamed Al Mamari, Sakshi Udeshi and Marc Astbury, with advisory help from authorized know-how specialists and platform analysis by HumanSignal.