Robots are coming into their GPT-3 period. For years, researchers have tried to coach robots utilizing the identical autoregressive (AR) fashions that energy giant language fashions (LLMs). If a mannequin can predict the following phrase in a sentence, it ought to be capable to predict the following transfer for a robotic arm. Nonetheless, a technical wall has blocked this progress: steady robotic actions are tough to show into discrete tokens.
A crew of researchers from Harvard College and Stanford College have launched a brand new framework known as Ordered Motion Tokenization (OAT) to bridge this hole.
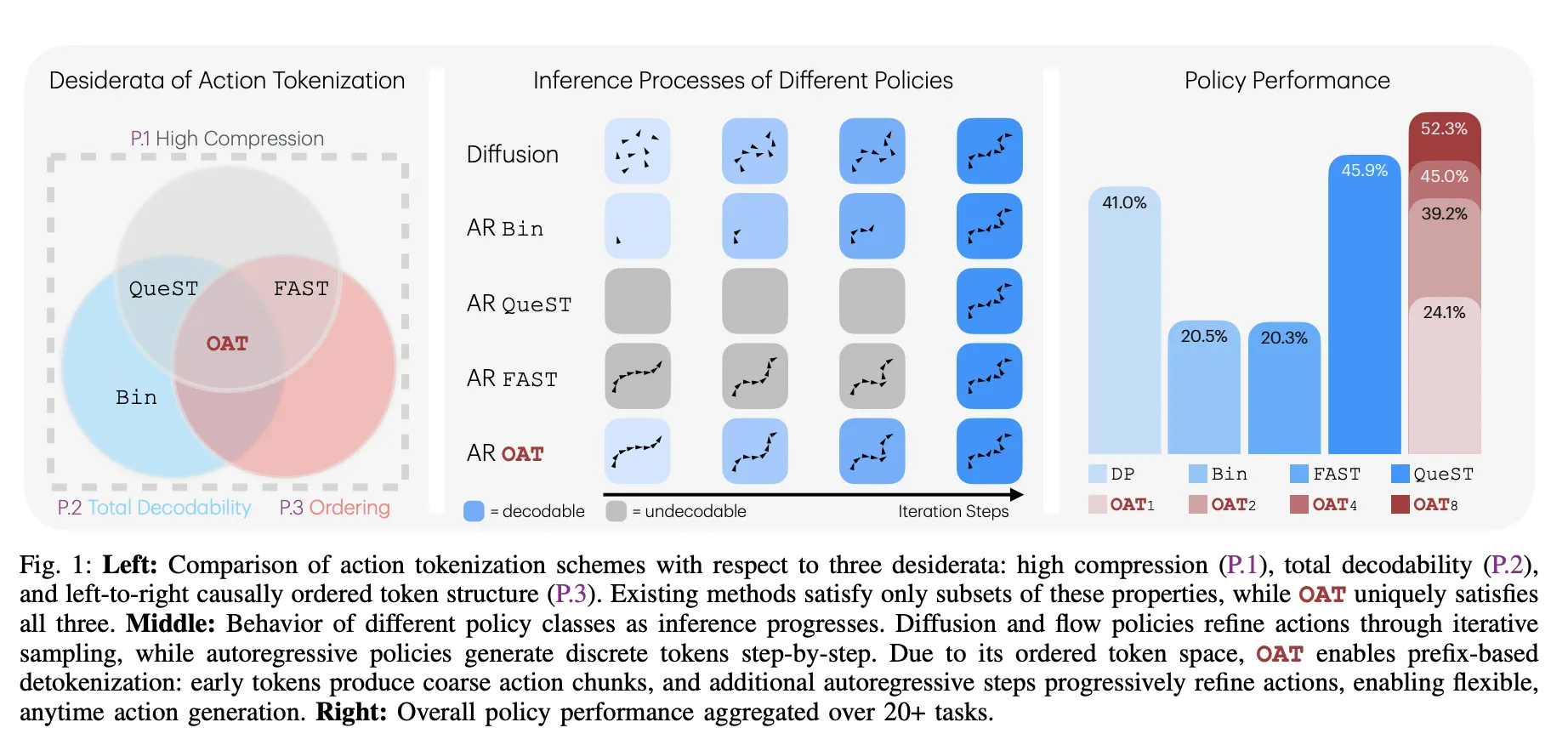

The Messy Actuality of Robotic Actions
Tokenization turns advanced knowledge right into a sequence of discrete numbers (tokens). For robots, these actions are steady indicators like joint angles. Earlier methods had deadly flaws:
- Binning: Turns each motion dimension right into a ‘bin.’ Whereas easy, it creates huge sequences that make coaching and inference sluggish.
- FAST (Frequency-space Motion Sequence Tokenization): Makes use of math to compress actions into frequency coefficients. It’s quick however usually produces ‘undecodable’ sequences the place small errors trigger the robotic to halt or transfer unpredictably.
- Discovered Latent Tokenizers: These use a discovered ‘dictionary’ of actions. They’re protected however lack a particular order, that means the mannequin treats early and late tokens as equally vital.


The Three Golden Guidelines of OAT
The analysis crew recognized 3 important properties—desiderata—for a practical robotic tokenizer:
- Excessive Compression (P.1): Token sequences should be quick to maintain fashions environment friendly.
- Whole Decodability (P.2): The decoder should be a complete perform, making certain each potential token sequence maps to a legitimate motion.
- Causal Ordering (P.3): Tokens should have a left-to-right construction the place early tokens seize international movement and later tokens refine particulars.
The Secret Sauce: Nested Dropout and Registers
OAT makes use of a transformer encoder with register tokens to summarize motion chunks. To pressure the mannequin to be taught ‘vital’ issues first, the analysis crew used a modern method known as Nested Dropout.


Breaking the Benchmarks
The analysis crew examined OAT throughout 20+ duties in 4 main simulation benchmarks. OAT constantly outperformed the industry-standard Diffusion Coverage (DP) and former tokenizers.
Efficiency Outcomes
| Benchmark | OAT Success Price | DP Success Price | Bin Token Depend | OAT Token Depend |
| LIBERO | 56.3% | 36.6% | 224 | 8 |
| RoboMimic | 73.1% | 67.1% | 224 | 8 |
| MetaWorld | 24.4% | 19.3% | 128 | 8 |
| RoboCasa | 54.6% | 54.0% | 384 | 8 |
‘Anytime’ Inference: Velocity vs. Precision
Essentially the most sensible good thing about OAT is prefix-based detokenization. For the reason that tokens are ordered by significance, you’ll be able to cease the mannequin early.
- Coarse Actions: Decoding simply 1 or 2 tokens offers the robotic a basic course rapidly, which is beneficial for low-latency duties.
- High-quality Actions: Producing all 8 tokens offers the high-precision particulars wanted for advanced insertions.
This permits for a clean trade-off between computation value and motion constancy that earlier fixed-length tokenizers couldn’t supply.
Key Takeaways
- Fixing the Tokenization Hole: OAT addresses a elementary limitation in making use of autoregressive fashions to robotics by introducing a discovered tokenizer that concurrently achieves excessive compression, whole decodability, and causal ordering.
- Ordered Illustration through Nested Dropout: By using nested dropout throughout coaching, OAT forces the mannequin to prioritize international, coarse movement patterns in early tokens whereas reserving later tokens for fine-grained refinements.
- Whole Decodability and Reliability: In contrast to prior frequency-domain strategies like FAST, OAT ensures the detokenizer is a complete perform, that means each potential token sequence generates a legitimate motion chunk, stopping runtime execution failures.
- Versatile ‘Anytime’ Inference: The ordered construction permits prefix-based decoding, permitting robots to execute coarse actions from only one or two tokens to save lots of computation or full eight-token sequences for high-precision duties.
- Superior Efficiency Throughout Benchmarks: Autoregressive insurance policies geared up with OAT constantly outperform diffusion-based baselines and different tokenization schemes, reaching a 52.3% combination success fee and superior leads to real-world ‘Choose & Place’ and ‘Stack Cups’ duties.
Try the Paper, Repo and Project Page. Additionally, be happy to comply with us on Twitter and don’t overlook to hitch our 100k+ ML SubReddit and Subscribe to our Newsletter. Wait! are you on telegram? now you can join us on telegram as well.




