Immediately we’ll take a quick take a look at some mortgage fee historical past to realize a little bit context for the place we stand right now. It’s all the time useful to know what got here earlier than so you possibly can higher guess what would possibly come after.
Nearly everybody is aware of that mortgage charges hit all-time report lows in 2021. However have you learnt what mortgage charges had been like within the early 1900s?
The 30-year fastened averaged 2.65% in the course of the week ending January seventh, 2021, its lowest level in historical past.
Later that yr, the 15-year fastened hit the bottom level ever, sinking to 2.10% in the course of the week ending July twenty ninth, 2021.
Some fortunate owners had been capable of snag fastened rates of interest beneath 2% for the following 15 to 30 years!
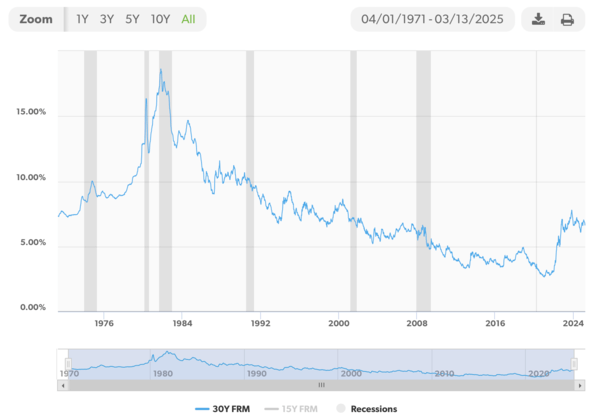
Freddie Mac’s Mortgage Price Statistics Began in 1971
- Most mortgage fee statistics are tied to Freddie Mac’s archive
- Sadly, it solely goes again to the yr 1971 which isn’t a lot to go on
- I wished to drill down a bit deeper to see what issues had been like previous to the 70s
- And see if I might discover information from earlier on within the twentieth century to realize extra perspective
The determine above come from Freddie Mac’s Primary Mortgage Market Survey, which solely dates again to 1971.
For the report, again in April of 1971, the primary month they started monitoring 30-year fastened mortgage charges, the nationwide common was 7.31%.
It went as excessive as 18.45% in October 1981 and as little as 2.65% in January 2021. That’s fairly a variety, clearly.
As you possibly can see within the chart, these 18% mortgage charges had been fairly short-lived, as had been the sub-3% mortgage charges. So in the end they are often thought-about outliers within the grand scheme of issues.
The 15-year fastened has solely been tracked by Freddie Mac since September 1991, when charges averaged 8.69%. In that very same month the 30-year fastened averaged 9.01%.
Anyway, I bear in mind some time again when fastened charges had been within the low 4% vary that the media was occurring about how charges hadn’t been this low because the Fifties.
Which made me surprise; the place had been they even pulling that historic mortgage fee information from?
I by no means actually took the time to see how low charges had been again then, however I lastly determined to do some digging to get a little bit extra info.
A Little Little bit of Mortgage Price Historical past
- Mortgage fee historical past stretches again almost a century
- However the very best data solely return to the early Seventies
- The 30-year fastened gained in recognition across the Fifties
- And charges reached a low round 1945 earlier than hitting new lows in 2021
My quest to seek out deeper mortgage fee historical past introduced me to a number of out-of-print volumes from the National Bureau of Economic Research, which appears to have the very best data on the market.
Sadly, the small print are nonetheless fairly murky at finest. You see, again then there have been different types of mortgages, not like those we use right now.
Whereas I don’t know when the very first 30-year fastened mortgage was created and issued (somebody please inform me), they had been believed to turn out to be widespread within the Fifties, which is why media references that decade.
Earlier than that point, it was widespread for entities like industrial banks and life insurance coverage firms to subject short-term balloon mortgages, .
These mortgages usually featured loans phrases as quick as three to 5 years, which might be frequently refinanced and by no means paid off.
These loans had been additionally underwritten at LTV ratios round 50%, which means it was fairly tough to get a house mortgage with out a sizable down fee. In different phrases, homeownership was reserved for the rich!
Later, as soon as the Great Depression struck, dwelling costs nosedived and scores of foreclosures flooded the housing market as a result of nobody might afford to make giant funds on their mortgages, particularly in the event that they didn’t have jobs.
Then got here FDR’s New Deal, which included the Home Owners’ Loan Corporation (HOLC) and the National Housing Act of 1934, each of which aimed to make housing extra inexpensive.
The HOLC, established in 1933, might clarify why long-term fixed-rate mortgages are in existence right now.
The aim of the HOLC was to refinance these outdated balloon mortgages into long-term, fully amortized loans, with phrases sometimes starting from 20 to 25 years. Not far off from the 30-year fastened we get pleasure from right now.
In a way, it jogs my memory of the Residence Inexpensive Refinance Program (HARP), which decrease mortgage charges for thousands and thousands of house owners in the course of the Nice Monetary Disaster (GFC).
Appears some issues by no means change, regardless of us considering it’s totally different this time…
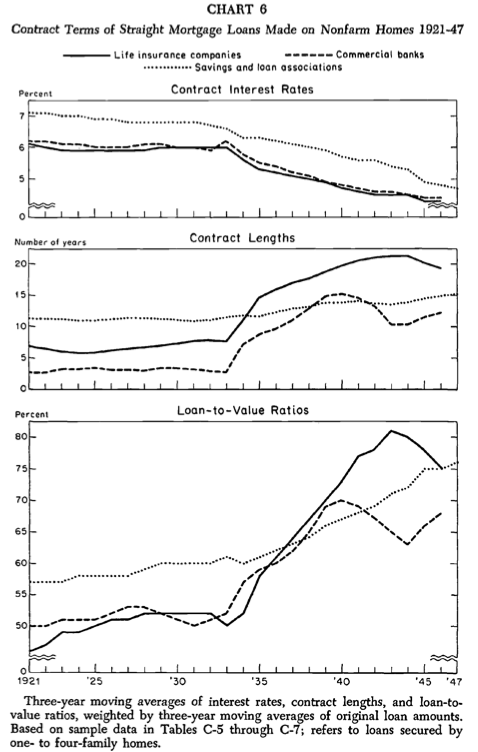
Mortgage Charges Got here Down as Mortgage Phrases and LTVs Elevated
- Homeownership turned extra inexpensive over time thanks to 3 essential issues:
- Decrease rates of interest
- Longer mortgage phrases
- And better LTVs (decrease down funds)
In 1934, the FHA and the Federal Financial savings and Mortgage Insurance coverage Company (FSLIC) had been created, and in 1938, Fannie Mae was born.
All of those entities primarily expanded credit score availability and led to extra liberal lending requirements for dwelling patrons.
Over time, mortgage interest rates got here down whereas LTV ratios and loan terms elevated, as you possibly can see from the charts beneath.
This made homeownership extra accessible for everybody, not simply these with the power to carry a large down fee to the desk.
Historic Mortgage Charges within the Early twentieth Century
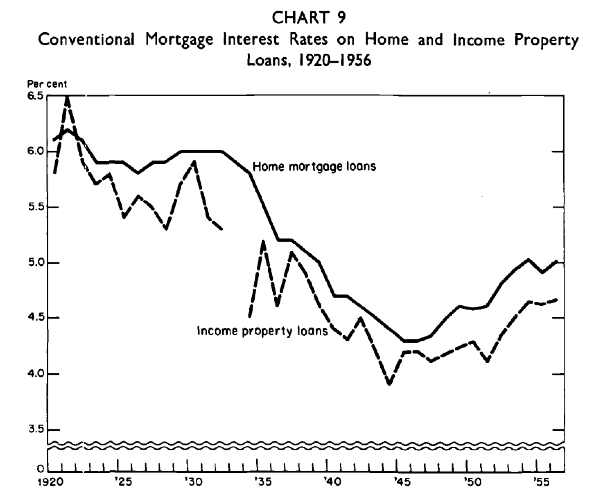
Whereas it’s onerous to get an apples-to-apples comparability of mortgage charges earlier than the arrival of the 30-year fastened, the Nationwide Bureau of Financial Analysis does have a chart detailing charges from 1920 to 1956.
From about 1920 till 1934, conventional mortgage charges averaged shut to six%, after which started to say no to a low level of slightly below 4.5%.
That is in all probability the reference level the media used after they stated charges hadn’t been this low in 60 years (again after they dropped within the early 2010s).
Mortgage Charges within the Twenties to Fifties
- We see a gentle drop in rates of interest from round 1935 to 1945
- Then a bottoming out for just a few years earlier than charges started their ascent to as high as 18% in the early 1980s
- Maybe as the results of World Warfare II ending and all of the related authorities debt and inflation that got here with it
- Exacerbated by a second spherical of inflation associated to the oil embargo that elevated enter prices for companies
Nevertheless, it’s unclear what kinds of mortgages these had been over this intensive time interval, and when the 30-year fastened truly turned the usual. However it does present for a little bit little bit of context.
The excellent news is as a result of mortgage charges went sub-3% within the early 2020s, we are able to in all probability take into account these to be the bottom on report, regardless of what occurred within the early twentieth century.
If we solely consider Freddie Mac’s information since 1971, the 30-year fastened has averaged about 7.75% over that interval.
However that features some very high-rate years within the Seventies and Nineteen Eighties and a few very low years within the 2010s and 2020s.
Many wish to discuss with charges right now as normal mortgage rates, however that doesn’t imply they aren’t quite a bit greater than they was once.
In truth, they almost tripled from 2021 to 2023, from 2.75% to eight%, so regular is a relative time period at finest.
Since 1990, the 30-year fastened has averaged nearer to six%, thanks partially to the report low charges seen over the previous decade.
So maybe mortgage charges are nearer to their long-term common right now within the high-6s. However with out dwelling value reduction and/or greater wages, affordability will stay traditionally low, which is why dwelling gross sales have plummeted.